文件路径写法详解:Windows vs Linux vs HTML
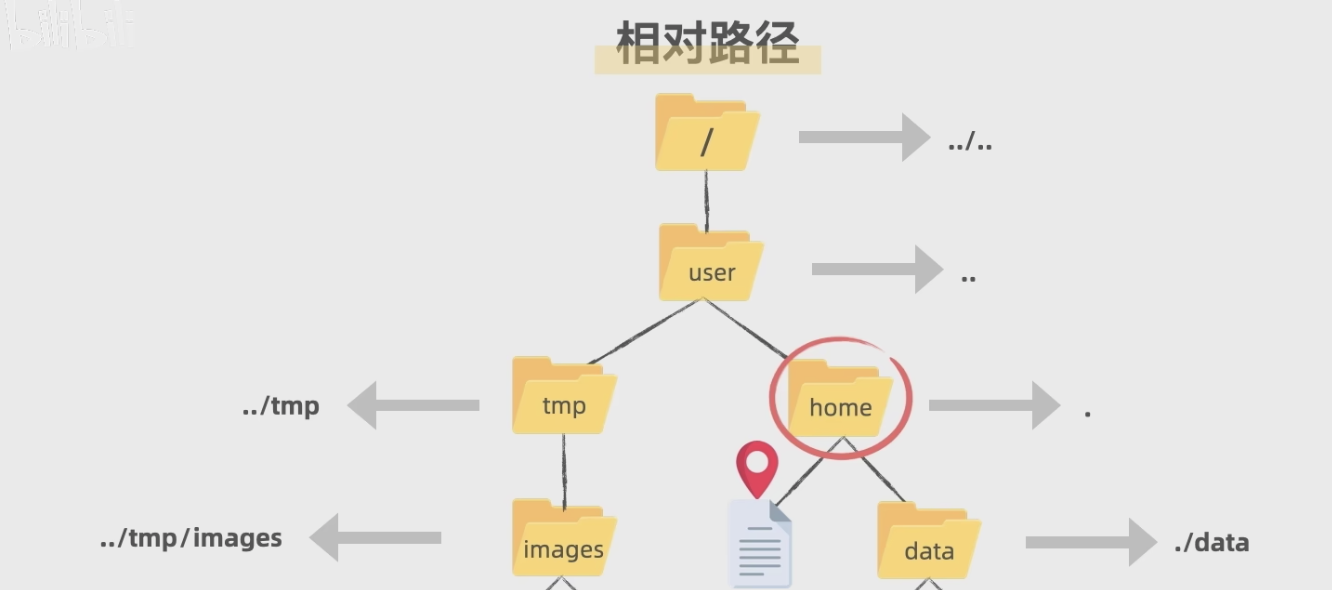 ## 一、操作系统路径差异
## 一、操作系统路径差异 1. 根目录表示
Linux/Mac(Unix-like系统)
bash
/ # 根目录
/home/user # 绝对路径
./file.txt # 当前目录下的file.txt
../file.txt # 上级目录下的file.txtWindows
cmd
C:\ # C盘根目录(绝对路径)
D:\ # D盘根目录
.\file.txt # 当前目录下的file.txt
..\file.txt # 上级目录下的file.txt2. 关键差异对比
| 特性 | Linux/Mac | Windows | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 目录分隔符 | / | \(也支持/) | Windows早期只用\,现代版本兼容/ |
| 根目录 | / | C:\, D:\等 | Windows按盘符分区 |
| 绝对路径 | /home/user | C:\Users\Name | |
| 当前目录 | . | . | 相同 |
| 上级目录 | .. | .. | 相同 |
二、HTML中的路径写法(与操作系统无关)
1. 相对路径(Relative Path)
html
<!-- 假设当前文件结构 -->
project/
├── index.html
├── css/
│ └── style.css
├── js/
│ └── main.js
└── images/
├── logo.png
└── bg.jpg(1) ./ - 当前目录(通常可省略)
html
<!-- 访问当前目录下的文件 -->
<img src="./logo.png"> <!-- 完整写法 -->
<img src="logo.png"> <!-- 通常省略./,默认就是当前目录 -->
<!-- 访问当前目录的css文件夹 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/style.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css"> <!-- 更常用 -->(2) ../ - 上级目录
html
<!-- 假设目录结构 -->
project/
├── pages/
│ └── about.html <!-- 当前文件 -->
└── images/
└── logo.pnghtml
<!-- 从about.html访问上级目录的images -->
<img src="../images/logo.png">
<!-- 多级上级 -->
<img src="../../parent-folder/image.png"> <!-- 向上两级 -->(3) ../../ 等多级上级
html
<!-- 目录越深,需要的..越多 -->
<img src="../../../assets/images/photo.jpg">2. 绝对路径(Absolute Path)
(1) 从根目录开始(网站根目录)
html
<!-- 以/开头:从网站根目录开始 -->
<img src="/images/logo.png"> <!-- 访问网站根目录的images -->
<link href="/css/style.css"> <!-- 访问网站根目录的css -->
<!-- 示例:访问 http://example.com/images/logo.png -->(2) 完整URL(绝对URL)
html
<!-- 包含协议、域名、路径 -->
<img src="https://example.com/images/logo.png">
<script src="http://cdn.example.com/js/jquery.js"></script>3. 特殊的 //(协议相对URL)
html
<!-- 使用当前页面的协议(自动选择http或https) -->
<img src="//cdn.example.com/images/logo.png">
<!-- 实际效果 -->
<!-- 如果当前页面是 http:// → 加载 http://cdn... -->
<!-- 如果当前页面是 https:// → 加载 https://cdn... -->
<!-- 常用场景:CDN资源,避免混合内容警告 -->
<script src="//code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script>三、路径类型对比表
| 写法 | 类型 | 含义 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
file.txt | 相对路径 | 当前目录下的file.txt | 默认方式 |
./file.txt | 相对路径 | 当前目录下的file.txt | 显式写法 |
folder/file.txt | 相对路径 | 当前目录下folder内的file.txt | |
../file.txt | 相对路径 | 上级目录下的file.txt | |
../../file.txt | 相对路径 | 上两级目录下的file.txt | |
/images/logo.png | 绝对路径 | 网站根目录的images文件夹 | 服务器根 |
C:\path\to\file | 绝对路径 | Windows本地绝对路径 | HTML中基本不用 |
/home/user/file | 绝对路径 | Linux本地绝对路径 | HTML中基本不用 |
//cdn.com/file | 协议相对 | 自动匹配当前页面协议 | CDN常用 |
https://... | 完整URL | 完整的网络地址 | 外部资源 |
四、实际应用场景
场景1:开发环境目录结构
my-project/
├── index.html
├── about.html
├── css/
│ ├── main.css
│ └── reset.css
├── js/
│ └── app.js
├── images/
│ ├── logo.png
│ └── banner.jpg
└── assets/
└── fonts/
└── font.ttf各文件中的路径引用:
index.html
html
<!-- 引入同级目录的文件 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/main.css">
<script src="js/app.js"></script>
<!-- 引入图片 -->
<img src="images/logo.png" alt="Logo">
<img src="images/banner.jpg" alt="Banner">
<!-- 跳转到about.html -->
<a href="about.html">关于我们</a>about.html
html
<!-- 从about.html引用css(路径不变,因为相对于网站根目录) -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/main.css">
<!-- 引用图片(路径不变) -->
<img src="images/logo.png" alt="Logo">css/main.css
css
/* CSS中的路径相对于CSS文件所在位置 */
body {
background-image: url("../images/bg.jpg"); /* 向上到my-project,再进images */
}
/* 引用字体文件 */
@font-face {
font-family: 'Custom';
src: url('../assets/fonts/font.ttf'); /* 向上到my-project,再进assets/fonts */
}场景2:多级目录结构
website/
├── index.html
├── products/
│ ├── phone.html
│ ├── laptop.html
│ └── images/
│ └── product1.jpg
├── blog/
│ ├── post1.html
│ └── post2.html
├── css/
│ └── style.css
└── js/
└── main.jsproducts/phone.html
html
<!-- 引用根目录的CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../css/style.css">
<!-- 解释:先向上到website,再进css -->
<!-- 引用自己的产品图片 -->
<img src="images/product1.jpg" alt="产品">
<!-- 解释:相对于phone.html,在products/images/ -->
<!-- 引用根目录的JS -->
<script src="../js/main.js"></script>
<!-- 跳转到首页 -->
<a href="../index.html">返回首页</a>
<!-- 跳转到博客 -->
<a href="../blog/post1.html">查看博客</a>五、常见错误和陷阱
错误1:混淆操作系统路径和Web路径
html
<!-- ❌ 错误:使用Windows路径(在Web服务器上无效) -->
<img src="C:\website\images\logo.png">
<!-- ✅ 正确:使用相对路径或Web绝对路径 -->
<img src="/images/logo.png">
<img src="../images/logo.png">错误2:路径大小写敏感问题
html
<!-- Linux服务器大小写敏感 -->
<img src="Images/Logo.png"> <!-- 如果实际是images/logo.png,会404 -->
<!-- Windows本地不敏感,但部署到Linux服务器会出错 -->错误3:忘记上级目录
html
<!-- 错误:在子目录中直接引用根目录文件 -->
<!-- 文件位置:products/phone.html -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css"> <!-- ❌ 找不到,会去products/css/找 -->
<!-- 正确 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../css/style.css"> <!-- ✅ -->六、最佳实践建议
1. 开发阶段
html
<!-- 使用相对路径,便于本地测试和移动 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
<script src="js/app.js"></script>
<!-- 图片也使用相对路径 -->
<img src="images/logo.png">2. 生产环境/部署
html
<!-- 使用根绝对路径,避免层级问题 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/style.css">
<img src="/static/images/logo.png">
<!-- 或使用CDN -->
<script src="https://cdn.example.com/js/app.min.js"></script>3. 路径配置技巧
对于动态网站(如PHP、Node.js),可以:
php
<!-- PHP中定义基础路径 -->
<?php
$baseUrl = '/my-project/';
if (isset($_SERVER['HTTPS']) && $_SERVER['HTTPS'] === 'on') {
$protocol = 'https';
} else {
$protocol = 'http';
}
$baseFullUrl = $protocol . '://' . $_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'] . $baseUrl;
?>
<link href="<?php echo $baseUrl; ?>css/style.css">4. 现代前端框架(Vue/React)
javascript
// React中(使用import)
import logo from './images/logo.png';
import './css/style.css';
// 在JSX中使用
function App() {
return <img src={logo} alt="Logo" />;
}
// Vue中
<template>
<img :src="require('./images/logo.png')" alt="Logo">
</template>七、调试技巧
1. 浏览器开发者工具
- 查看网络面板,确认资源是否正确加载
- 检查控制台是否有404错误
- 鼠标悬停链接查看完整URL
2. 打印当前路径
javascript
// 在控制台查看当前路径
console.log('当前页面URL:', window.location.href);
console.log('当前目录:', window.location.pathname);
// 获取当前文件的目录
const currentDir = window.location.pathname.substring(
0, window.location.pathname.lastIndexOf('/') + 1
);
console.log('当前文件所在目录:', currentDir);3. 使用base标签简化路径
html
<head>
<base href="https://example.com/my-project/">
<!-- 或相对路径 -->
<base href="/my-project/">
</head>
<body>
<!-- 所有相对路径都会基于base -->
<img src="images/logo.png"> <!-- 实际访问:/my-project/images/logo.png -->
</body>八、快速记忆口诀
- 同级文件:直接写文件名,或
./开头 - 子文件夹:
文件夹名/文件 - 上级文件夹:
../开头,每多一级加一个../ - 网站根目录:
/开头(指服务器根目录,不是系统根目录) - 网络资源:
//开头(协议自适应)或完整https:// - 本地路径:开发时用相对路径,上线后调整
记住:HTML中的路径始终是基于URL的,不是基于文件系统的! 这是理解路径的关键。